Jews in Germany
|
Jews have lived in Germany for over 1700 years, through both periods of tolerance and spasms of antisemitic violence. In the nineteenth century, the Reform Jewish movement began in Germany and saw a flowering of intellectual life which saw the assimilation of many German Jews into the cultural and intellectual life of the wider society. However, this was followed in the twentieth century by the worst episode of anti-Semitic violence in history during the Third Reich which itself culminated in the Holocaust and the near-destruction of the Jewish community in Germany and much of Europe. Today, over 200,000 Jews or persons of Jewish descent live in Germany, one of the largest Jewish populations in a European country.[1] Following the victimization of what was probably the most assimilated Jewish community in the world, the movement to found an independent state for Jews where they would be free from persecution gained momentum. Others questioned the value of what they saw as compromises made by Reform Judaism, when these did not guarantee the safety, security and survival of the Jews.
Early settlements
The date of the first settlement of Jews in the regions the Romans called Germania Superior, Germania Inferior, and Germania Magna is not known. The first authentic document relating to a large and well-organized Jewish community in these regions dates from 321 C.E., and refers to Cologne on the Rhine; it indicates that the legal status of the Jews there was the same as elsewhere in the Roman Empire. They enjoyed some civil liberties, but were restricted regarding the dissemination of their faith, the keeping of Christian slaves, and the holding of office under the government.
Jews were otherwise free to follow any occupation open to their fellow citizens, and were engaged in agriculture, trade, industry, and gradually money-lending. These conditions at first continued in the subsequently established Germanic kingdoms under the Burgundians and Franks, for ecclesiasticism took root slowly. The Merovingian rulers who succeeded to the Burgundian empire, were devoid of fanaticism, and gave scant support to the efforts of the Church to restrict the civic and social status of the Jews.
Under Charlemagne
Charlemagne readily made use of the Church for the purpose of infusing coherence into the loosely joined parts of his extensive empire, by any means a blind tool of the canonical law. He made use of the Jews so far as suited his diplomacy, sending, for instance, a Jew as interpreter and guide with his embassy to Harun al-Rashid. Yet even then a gradual change occurred in the lives of the Jews. Unlike the Franks, who were liable to be called to arms at any moment in those tumultuous times, the Jews were exempt from military service; hence, trade and commerce were left almost entirely in their hands, and they secured the remunerative monopoly of money-lending when the Church forbade Christians to take usury. This decree caused the Jews to be sought everywhere as well as avoided, for their capital was indispensable while their business was viewed as disreputable. This curious combination of circumstances increased their influence. They went about the country freely, settling also in the eastern portions. Aside from Cologne, the earliest communities seem to have been established in Worms and Mainz.
Up to the Crusades
The status of the German Jews remained unchanged under Charlemagne’s weak successor Louis the Pious (778 – 840). They were unrestricted in their commerce, merely paying into the state treasury a somewhat higher tax than did the Christians. A special officer, the Judenmeister, was appointed by the government to protect their privileges. The later Carolingians, however, fell more and more in with the demands of the Church. The bishops, who were continually harping at the synods on the anti-Semitic decrees of the canonical law, finally brought it about that the majority Christian populace was filled with mistrust against the Jewish unbelievers. This feeling, among both princes and people, was further stimulated by the attacks on the civic equality of the Jews. Beginning with the tenth century, Holy Week became more and more a period of persecution for them. Yet the Saxon (Ottonian) emperors, beginning with Henry the Fowler did not treat the Jews badly, exacting from them merely the taxes levied upon all other merchants. Although they were as ignorant as their contemporaries in secular studies, they could read and understand the Hebrew prayers and the Bible in the original text. Halakic studies began to flourish about 1000.
At that time Rabbi Gershom ben Judah was teaching at Metz and Mayence, gathering about him pupils from far and near. He is described as a model of wisdom, humility, and piety, and is praised by all as a “lamp of the Exile.” He first stimulated the German Jews to study the treasures of their religious literature.
This continuous study of the Torah and the Talmud produced such a devotion to their faith that the Jews considered life without their religion not worth living; but they did not realize this clearly until the time of the Crusades, when they were often compelled to choose between life and faith.
A period of massacres (1096–1349)
The wild excitement to which the Germans had been driven by exhortations to take the cross first broke upon the Jews, the nearest representatives of an execrated opposition faith. Entire communities, like those of Treves, Speyer, Worms, Mayence, and Cologne, were slain, except where the slayers were anticipated by the deliberate self-destruction of their intended victims. About 12,000 Jews are said to have perished in the Rhenish cities alone between May and July 1096. These outbreaks of popular passion during the Crusades influenced the future status of the Jews. To salve their consciences the Christians brought accusations against the Jews to prove that they had deserved their fate; imputed crimes, like desecration of the host, ritual murder, poisoning of wells, and treason, brought hundreds to the stake and drove thousands into exile. They were accused of having caused the inroads of the Mongols, even though they suffered equally with the Christians. When the Black Death swept over Europe in 1348–1349, the Jews were accused of well poisoning, and a general slaughter began throughout the Germanic and contiguous provinces, causing a massive exodus east to Poland, where they at first were warmly greeted by the Polish King, forming the future foundations of the largest Jewish community in Europe.
In the Holy Roman Empire
Nevertheless, the legal and civic status of the Jews was undergoing a transformation. They found a certain degree of protection with the emperor of the Holy Roman Empire, who claimed the right of possession and protection of all the Jews of the empire in virtue of being the successor of the emperor Titus, who was said to have acquired the Jews as his private property. The German emperors claimed this "right of possession" more for the sake of taxing the Jews than of protecting them. Ludwig the Bavarian especially exerted his ingenuity in devising new taxes. In 1342 he instituted the “golden sacrificial penny” and decreed that every year all the Jews should pay to the emperor one kreutzer in every gulden of their property in addition to the taxes they were paying to the state and municipal authorities.
The emperors of the house of Luxemburg devised still other means of taxation. They turned their prerogatives in regard to the Jews to further account by selling at a high price to the princes and free towns of the empire the valuable privilege of taxing and mulcting the Jews. On the reorganization of the empire in 1356, Charles IV, by the Golden Bull, granted this privilege to the seven electors of the empire. From this time onward the Jews of Germany gradually passed in increasing numbers from the authority of the emperor to that of the lesser sovereigns and of the cities. For the sake of sorely needed revenue the Jews were now invited, with the promise of full protection, to return to those districts and cities from which they had shortly before been cruelly expelled; but as soon as they had acquired some property they were again plundered and driven away. These episodes thenceforth constituted the history of the German Jews. Emperor Wenceslaus was most expert in transferring to his own coffers gold from the pockets of rich Jews. He made compacts with many cities, estates, and princes whereby he annulled all outstanding debts to the Jews in return for a certain sum paid to him, adding that anyone who should nevertheless help the Jews to collect their debts should be dealt with as a robber and peacebreaker, and be forced to make restitution. This decree, which for years injured the public credit, impoverished thousands of Jewish families during the close of the fourteenth century.
Nor did the fifteenth century bring any amelioration. What happened in the time of the Crusades happened again. During the war upon the Hussite heretics became the signal for the slaughter of the unbelievers. The Jews of Austria, Bohemia, Moravia, and Silesia passed through all the terrors of death, forced baptism, or voluntary immolation for the sake of their faith. When the Hussites made peace with the Church, the pope sent the Franciscan monk Capistrano to win the renegades back into the fold and inspire them with loathing for heresy and unbelief; 41 martyrs were burned in Breslau alone, and all Jews were forever banished from Silesia. The Franciscan monk Bernardinus of Feltre brought a similar fate upon the communities in southern and western Germany.[2] As a consequence of the fictitious confessions extracted under torture from the Jews of Trent, the populace of many cities, especially of Ratisbon, fell upon the Jews and massacred them.
The end of the fifteenth century, which brought a new epoch for the Christian world, brought no relief to the Jews. They remained the victims of a religious hatred that ascribed to them all possible evils. When the established Church, threatened in its spiritual power in Germany and elsewhere, prepared for its conflict with the culture of the Renaissance, one of its most convenient points of attack was rabbinic literature. At this time, as once before in France, Jewish converts spread false reports in regard to the Talmud. But an advocate of the book arose in the person of Johannes Reuchlin (1455 - 1522), the German humanist, who was the first one in Germany to include the Hebrew language among the humanities. His opinion, though strongly opposed by the Dominicans and their followers, finally prevailed when the humanistic Pope Leo X permitted the Talmud to be printed in Italy.
During the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries
The feeling against the Jews themselves, however, remained the same. During the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries they were still subject to the will of the princes and free cities, both in Catholic and in Protestant countries. Martin Luther (1483-1645) advocated in “That Jesus Was Born A Jews” (1523) that Christian love, not “papal law” should guide Christians in their dealings with Jews.[3] Later, in his “The Jews and Their Lies” he changed his tune, and suggested that it would “honor our Lord” were Christians to “set fire to their synagogues and … bury … and cover wth dirt whatever will not burn, so that no man will ever again see a stone or a cinder of them.”[4] The German emperors were not always able to protect them, even when they desired to do so, as did the chivalrous Emperor Maximilian I; they could not prevent the accusations of ritual murder and desecration of the host. The unending religious controversies that rent the empire and finally led to the Thirty Years’ War further aggravated the position of the Jews, who were made the prey of each party in turn. The emperors even occasionally expelled their kammerknechte from their crown lands, although they still assumed the office of protector. Ferdinand I expelled the Jews from Lower Austria and Görz, and would have carried out his vow to banish them also from Bohemia had not the noble Mordecai Ẓemaḥ Cohen of Prague induced the pope to absolve the emperor from this vow. Emperor Leopold I expelled them in 1670 from Vienna and the Archduchy of Austria, in spite of their vested rights and the intercession of princes and ecclesiastics; the exiles were received in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. The Great Elector Frederick William (1620–1688), deciding to tolerate all religious beliefs impartially, protected his new subjects against oppression and slander. In spite of the civic and religious restrictions to which they were subjected even here, the Jews of this flourishing community gradually attained to a wider outlook, although their one-sided education, the result of centuries of oppression, restricted them in European culture and kept them in intellectual bondage.
Migration of Polish and Lithuanian Jews to Germany
The atrocities of Chmielnicki[5] and his Cossacks drove the Polish Jews back into western Germany. This trend accelerated throughout the eighteenth century as parts of Germany began to readmit Jews, and with the worsening conditions in Poland after the Partition of Poland in 1765 and 1795 between Prussia, Austria, and Russia.
Jewish life through the Holy Roman Empire

The Jews had kept their piety and their intellectual activity. They were devoted to the study of the Halakah. In the eleventh century Rabbi Gershom’s[6]pupils had been the teachers of Rashi, and his commentaries on the Bible and Talmud marked out new paths for learning. The German Jews contributed much to the spread and completion of these commentaries. Beginning with the 12th century they worked independently, especially in the fields of Haggadah and ethics. R. Simon ha-Darshan’s Yalḳuṭ (c. 1150), the Book of the Pious by R. Judah ha-Ḥasid of Ratisbon (c. 1200), the Salve-Mixer (Rokeaḥ) of R. Eleasar of Worms (c. 1200), the halakic collection Or Zarua of R. Isaac of Vienna (c. 1250), the responsa of Rabbi Meïr of Rothenburg (died 1293), are enduring monuments of German Jewish industry. Even the horrors of the Black Death could not completely destroy this literary activity. Profound and wide scholarship was less common after the middle of the fourteenth century, which led to the institution of allowing only those scholars to become rabbis who could produce a written authorization to teach (hattarat hora’ah), issued by a recognized master. To this period of decline belong also a number of large collections of responsa and useful commentaries on earlier halakic works. The customs and ordinances relating to the form and order of worship were especially studied in this period, and were definitely fixed for the ritual of the synagogues of western and eastern Germany by Jacob Mölln (Maharil) and Isaac Tyrnau. As it was difficult to produce any new works in the field of the Halakah, and as the dry study of well-worn subjects no longer satisfied, scholars sought relief in the interpretations and traditions embodied in the Cabala. There arose a new, ascetic view of life that found literary expression in the Shene Luḥot ha-Berit by Rabbi Isaiah Horovitz of Frankfurt am Main (died 1626), and that appealed especially to the pietistic German Jews. The end and aim of existence were now sought in the aspiration of the soul toward its fountainhead, combined with the endeavor to saturate the earthly life with the spirit of God. By a continuous attitude of reverence to God, by lofty thoughts and actions, the Jew was to rise above the ordinary affairs of the day and become a worthy member of the kingdom of God. Every act of his life was to remind him of his religious duties and stimulate him to mystic contemplation.
Separation from the world
The oppressions under which the Jews suffered encouraged an austere view of life. They lived in fear in their Jews’ streets, subsisting on what they could earn as peddlers and as dealers in old clothes. Cut off from all participation in public and municipal life, they had to seek in their homes compensation for the things denied them outside. Their family life was intimate, beautified by faith, industry, and temperance. They were loyal to their community. In consequence of their complete segregation from their Christian fellow citizens, the German speech of the ghetto was interladen with Hebraisms, and also with Slavonic elements since the seventeenth century. When the atrocities of Chmielnicki and his Cossacks drove the Polish Jews back into western Germany. As the common people understood only the books written in this peculiar dialect and printed in Hebrew characters, a voluminous literature of edifying, devotional, and belletristic works sprang up in Judæo-German to satisfy the needs of these readers. Although this output was one-sided, presupposing almost no secular knowledge, its importance in the history of Jewish culture must not be underestimated. The study of the Bible, Talmud, and halakic legal works, with their voluminous commentaries, preserved the plasticity of the Jewish mind, until a new Moses came to lead his coreligionists out of intellectual bondage toward modern culture.
From Moses Mendelssohn (1778) to the Nazis (1933)
Moses Mendelssohn
Moses Mendelssohn located with true insight the point of departure for the regeneration of Jewish life. The Middle Ages, which could take from the Jews neither their faith nor their past intellectual achievements, had yet deprived them of the chief means (namely, the vernacular) of comprehending the intellectual labors of others. The chasm that in consequence separated them from their educated fellow citizens was bridged by Mendelssohn’s translation of the Torah into German. This book became the manual of the German Jews, teaching them to write and speak the German language, and preparing them for participation in German culture and secular science. Mendelssohn lived to see the first fruits of his endeavors. In 1778 his friend David Friedländer founded the Jewish free school in Berlin, this being the first Jewish educational institution in Germany in which instruction, in scripture as well as in general science, was carried on in German only. Similar schools were founded later in the German towns of Breslau (1792), Seesen (1801), Frankfurt (1804), and Wolfenbüttel (1807), and the Galician towns of Brody and Tarnopol (1815). In 1783 the periodical Der Sammler was issued with the view of providing general information for adults and enabling them to express themselves in pure, harmonious German.
A youthful enthusiasm for new ideals at that time pervaded the entire civilized world; all religions were recognized as equally entitled to respect, and the champions of political freedom undertook to restore the Jews to their full rights as men and citizens. The humane Austrian Emperor Joseph II was foremost in espousing these new ideals. As early as 1782 he issued the Patent of Toleration for the Jews of Lower Austria, thereby establishing the civic equality of his Jewish subjects. Prussia conferred citizenship upon the Prussian Jews in 1812, though this by no means included full equality with other citizens. The German federal edicts of 1815 merely held out the prospect of full equality; but it was not realized at that time, and even the promises that had been given were modified. In Austria many laws restricting the trade and traffic of Jewish subjects remained in force down to the middle of the nineteenth century, in spite of the patent of toleration. Some of the crown lands, as Styria and Upper Austria, forbade any Jews to settle within their territory; in Bohemia, Moravia, and Silesia many cities were closed to them. The Jews were, in addition, burdened with heavy taxes and imposts.
In the German kingdom of Prussia, also, the government modified materially the promises made in the disastrous year 1813. The promised uniform regulation of Jewish affairs was time and again postponed. In the period between 1815 and 1847 there were no less than 21 territorial Jews’ laws in the eight provinces of the Prussian state, each having to be observed by a part of the Jewish community. There was at that time no official authorized to speak in the name of all German Jews. Nevertheless, a few courageous men came forward to maintain their cause, foremost among them being Gabriel Riesser, a Jewish lawyer of Hamburg (died 1863), who demanded full civic equality for his race from the German princes and peoples. He aroused public opinion to such an extent that this equality was granted in Prussia on April 6, 1848, and in Hanover and Nassau on September 5 and on December 12, respectively. In Württemberg equality was conceded on December 3, 1861; in Baden on October 4, 1862; in Holstein on July 14, 1863; and in Saxony on December 3, 1868. After the establishment of the North German Union by the law of July 3, 1869, all existing restrictions imposed on the followers of different religions were abolished; this decree was extended to all the provinces of the German empire after the events of 1870.
The Jewish enlightenment in Germany
The intellectual development of the Jews kept pace with their civic enfranchisement. Recognizing that pursuit of modern culture would not at once assure them the civic status they desired, their leaders set themselves to reawaken Jewish self-consciousness by applying the methods of modern scholarship to the study of Jewish sources, and to stimulate the rising generation by familiarizing them with the intellectual achievements of their ancestors, which had been accumulating for thousands of years; and at the same time they sought to rehabilitate Judaism in the eyes of the world. The leader of this new movement and the founder of modern Jewish science was Leopold Zunz (1794–1886), who united broad general scholarship with a thorough knowledge of the entire Jewish literature and who, with his contemporary Solomon Judah Löb Rapoport of Galicia (1790–1867), especially aroused their coreligionists in Germany, Austria, and Italy. Arnheim wrote a scholarly manual of the Hebrew language [7] Julius Fürst and David Cassel compiled Hebrew Dictionaries[8] Fürst and Bernhard Bär compiled concordances to the entire Bible.[9] Wolf Heidenheim and Seligmann Baer edited correct Masoretic texts of the Bible; Solomon Frensdorff subjected the history of the Masorah to a thoroughly scientific investigation; the Bible was translated into German under the direction of Zunz and Salomon; Ludwig Philippson, Solomon Hirschheimer, and Julius Fürst wrote complete Biblical commentaries; H. Grätz and S.R. Hirsch dealt with some of the Biblical books; Zacharias Frankel and Abraham Geiger investigated the Aramaic and Greek translations. Nor was the traditional law neglected. Jacob Levy compiled lexicographical works to the Talmud and Midrashim. Michael Sachs and Joseph Perles investigated the foreign elements found in the language of the Talmud. Numerous and, on the whole, excellent editions of halakic and haggadic midrashim were issued—for instance, Zuckermandel’s edition of the Tosefta and Theodor’s edition of Midrash Rabbah to Genesis. Zacharias Frankel wrote an introduction to the Mishnah and to the Jerusalem Talmud, and David Hoffmann and Israel Lewy investigated the origin and development of the Halakah.
Religio-philosophical literature was also assiduously cultivated, and the original Arabic texts of Jewish religious philosophers were made accessible. M.H. Landauer issued Saadia Gaon’s works, and H. Hirschfeld the works of Judah ha-Levi. M. Joel and I. Guttmann investigated the works of Jewish thinkers and their influence on the general development of philosophy, while S. Hirsch attempted to develop the philosophy of religion along the lines laid down by Hegel, and Solomon Steinheim propounded a new theory of revelation in accordance with the system of the synagogue.
Reorganization of the German Jewish community
The enfranchisement of the Jews and the reflorescence of Jewish science led to a reorganization of their institutions with a view to transmitting the ancient traditions intact with the new generations. Opinions differed widely as to the best methods of accomplishing this object. While Geiger and Holdheim were ready to meet the modern spirit of liberalism, Samson Raphael Hirsch defended the customs handed down by the fathers. And as neither of these two tendencies was followed by the mass of the faithful, Zacharias Frankel initiated a moderate Reform movement on a historical basis, in agreement with which the larger German communities reorganized their public worship by reducing the medieval payyeṭanic additions to the prayers, introducing congregational singing and regular sermons, and requiring scientifically trained rabbis.
In general, it was easier to agree upon the means of training children for the Reformed worship and awakening the interest of adults in Jewish affairs. The religious schools were an outcome of the desire to add religious instruction to the secular education of Jewish children prescribed by the state. As the Talmudic schools, still existing in Germany in the first third of the 19th century, were gradually deserted; rabbinical seminaries were founded, in which Talmudic instruction followed the methods introduced by Zacharias Frankel in the Jewish Theological Seminary opened at Breslau in 1854. Since then special attention has been devoted to religious literature. Textbooks on religion and specifically on Biblical and Jewish history, as well as aids to the translation and explanation of the Bible and the prayer-books, were compiled to meet the demands of modern pedagogics. Pulpit oratory began to flourish as never before, foremost among the great German preachers being M. Sachs and M. Joël. Nor was synagogal music neglected, Louis Lewandowski especially contributing to its development.
The public institutions of the Jewish communities served to supplement the work of teachers and leaders, and to promote Jewish solidarity. This was the primary object of the Jewish press, created by Ludwig Philippson. In 1837 he founded the Allgemeine Zeitung des Judenthums, which has been followed by a number of similar periodicals. They had succeeded in preserving a certain unity of religious opinion and conviction among the Jews, with the gratifying result of unity of action for the common good. Societies for the cultivation of Jewish literature were founded, as well as associations of teachers, rabbis, and leaders of congregations.
Birth of the Reform Movement
In response to the Enlightenment and the emancipation, elements within German Jewry sought to reform Jewish belief and practice, starting the Jewish Reform Movement. In light of modern scholarship, these German Jews denied divine authorship of the Torah, declared only those biblical laws concerning ethics to be binding, and stated that the rest of halakha (Jewish law) need no longer be viewed as normative. Circumcision was abandoned, rabbis wore vestments modeled after Protestant ministers, and instrumental accompaniment—banned in Jewish Sabbath worship since the destruction of the Second Temple in 70 C.E.—reappeared in Reform synagogues, most often in the form of a pipe organ. The traditional Hebrew prayer book (the Siddur) was replaced with a German text which truncated or altogether excised most parts of the traditional service. Reform synagogues began to be called temples, a term reserved in more traditional Judaism for the Temple in Jerusalem. The practice of Kashrut (keeping kosher) was abandoned as an impediment to spirituality. The early Reform movement renounced Zionism and declared Germany to be its new Zion. This anti-Zionist view is no longer held; see below. One of the most important figures in the history of Reform Judaism is the radical reformer Samuel Holdheim.
Freedom and repression (1815–1930s)
Napoleon emancipated the Jews across Europe, but with Napoleon’s fall in 1815, growing nationalism resulted in increasing repression. In 1819, Hep-Hep riots—according to one interpretation from the Latin Hierosolyma est perdita (Jerusalem is lost), the rallying cry of the Crusaders, but more likely derived from the traditional herding cries of the German Folk—destroyed Jewish property and killed many Jews. The Revolution of 1848 swung the pendulum back towards freedom for the Jews, but the financial crisis of 1873 created another era of repression. Starting in the 1870s, anti-Semites of the völkisch movement were the first to describe themselves as such, because they viewed Jews as part of a Semitic race that could never be properly assimilated into German society. Such was the ferocity of the anti-Jewish feeling of the völkisch movement that by 1900, the term anti-Semitic had entered the English language to describe anyone who had anti-Jewish feelings. However, despite massive protests and petitions, the völkisch movement failed to persuade the government to revoke Jewish emancipation, and in the 1912 Reichstag elections, the parties with völkisch-movement sympathies suffered a temporary defeat. In the 1920s, German cities were still expelling Jews. The granting of full civil rights was opposed by many eminent intellectuals, although this was granted in 1848. In 1881, Otto von Bismarck received a petition with 250,000 signatures demanding severe anti-Jewish measures. The petition said that Jews were “inferior and depraved”[10]
Jews experienced a period of legal equality from 1848 until the rise of Nazi Germany. In the opinion of historian Fritz Stern, by the end of the nineteenth century, what had emerged was a Jewish-German symbiosis, where German Jews had merged elements of German and Jewish culture into a unique new one.
A higher percentage of German Jews fought in World War I than that of any other ethnic, religious or political group in Germany—in fact, some 12,000 died for their country.[11][12] The chancellor during the first two years of the war, Theobald von Bethmann Hollweg, was the son and grandson of German Jewish public servants. Ironically, it was a Jewish lieutenant, Hugo Gutmann, who awarded the Iron Cross, First Class, to a 29-year-old corporal named Hitler. When Hitler came to power in 1933, Gutmann left Germany and escaped to the United States.
In October 1916, the German Military High Command administered Judenzählung (census of Jews). Designed to confirm accusations of the lack of patriotism among German Jews, the census disproved the charges, but its results were not made public.[13] Denounced as a “statistical monstrosity”,[14] the census was a catalyst to intensified antisemitism and social myths such as the “stab-in-the-back legend” (Dolchstosslegende).[15]
German Jews enjoyed full equality in the Weimar Republic, many receiving high political positions such as foreign minister and vice chancellor. The Weimar constitution was the work of a German Jew, Hugo Preuss, who later became minister of the interior. Marriages between Jews and non-Jews became somewhat common from the nineteenth century; for example, the wife of German Chancellor Gustav Stresemann was Jewish.
Jews under the Nazis (1930s–1940)
In 1933, persecution of the Jews became active Nazi policy, but at first laws were not as rigorously obeyed and were not as devastating as in later years.
On April 1, 1933, Jewish doctors, shops, lawyers and stores were boycotted. Only six days later, the Law for the Restoration of the Professional Civil Service was passed, banning Jews from being employed in government. This laws meant that Jews were now indirectly and directly dissuaded or banned from privileged and upper-level positions reserved for “Aryan” Germans. From then on, Jews were forced to work at more menial positions, beneath non-Jews.
On August 2, 1934, President Paul von Hindenburg died. No new president was appointed; instead the powers of the chancellor and president were combined into the office of Führer. This, and a tame government with no opposition parties, allowed Adolf Hitler totalitarian control of law making. The army also swore an oath of loyalty personally to Hitler, giving him power over the military and allowing him to easily create more pressure on the Jews than ever before.
In 1935 and 1936, persecution of the Jews increased apace. In May 1935, Jews were forbidden to join the Wehrmacht (Armed Forces), and that year, anti-Jewish propaganda appeared in Nazi German shops and restaurants. The Nuremberg Racial Purity Laws were passed around the time of the great Nazi rallies at Nuremberg; On September 15, 1935, the "Law for the Protection of German Blood and Honour" was passed, preventing marriage between any Jew and non-Jew. At the same time the Reich Citizenship Law was passed and was reinforced in November by a decree, stating that all Jews, even quarter- and half-Jews, were no longer citizens (Reichsbürger) of their own country (their official status became Reichsangehöriger, “subject of the state”). This meant that they had no basic civil rights, such as the right to vote. (But at this time the right to vote for the non-Jewish Germans only meant the obligation to vote for the Nazi party.) This removal of basic citizens’ rights preceded harsher laws to be passed in the future against Jews. The drafting of the Nuremberg Laws is often attributed to Hans Globke.
In 1936, Jews were banned from all professional jobs, effectively preventing them from exerting any influence in education, politics, higher education and industry. Because of this, there was nothing to stop the anti-Jewish actions that spread across the Nazi-German economy.
After the Night of the Long Knives, the Schutzstaffel (SS) became the dominant policing power in Germany. Reichsführer-SS Heinrich Himmler was eager to please Hitler and so willingly obeyed his orders. Since the SS had been Hitler’s personal bodyguard, its members were far more loyal and professional than those of the Sturmabteilung (SA) had been. Because of this, they were also supported by the army, which was now more willing to agree with Hitler’s decisions than when the SA was dominant.
All of this allowed Hitler more direct control over government and political attitude towards Jews in Nazi Germany. In 1937 and 1938, harsh new laws were implemented, and the segregation of Jews from the true “Aryan” German population was started. In particular, Jews were penalized financially for their perceived racial status.
On June 4, 1937 a young Jewish German, Helmut Hirsch, was executed for being involved in a plot to kill the Nazi leadership—including Hitler.
As of March 1, 1938, government contracts could no longer be awarded to Jewish businesses. On September 30, “Aryan” doctors could only treat “Aryan” patients. Provision of medical care to Jews was already hampered by the fact that Jews were banned from being doctors or having any professional jobs.
Beginning August 17, 1938, Jews had to add Israel (males) or Sarah (females) to their names, and a large J was to be imprinted on their passports beginning October 5. On November 15 Jewish children were banned from going to normal schools. By April 1939, nearly all Jewish companies had either collapsed under financial pressure and declining profits, or had been persuaded to sell out to the Nazi German government. This further reduced Jews’ rights as human beings; they were in many ways officially separated from the German populace.
The increasingly totalitarian, militaristic regime that was being imposed on Germany by Hitler allowed him to control the actions of the SS and the military. On November 7, 1938, a young Polish Jew, Herschel Grynszpan, attacked and shot two German officials in the Nazi German embassy in Paris. (Grynszpan was angry about the treatment of his parents by the Nazi Germans). On November 9 the German Attache, vom Rath, died. Goebbels issued instructions that demonstrations against Jews be organized and undertaken in retaliation throughout Germany. The SS ordered the Night of Broken Glass (Kristallnacht) to be carried out that night, November 9–10. The storefronts of Jewish shops and offices were smashed and vandalized, and many synagogues were destroyed by fire. Approximately 100 Jews were killed, and another 20,000 arrested, some of whom were sent to the newly-formed concentration camps. Many Germans were disgusted by this action when the full extent of the damage was discovered, so Hitler ordered it to be blamed on the Jews. Collectively, the Jews were made to pay back one billion Reichsmark in damages, the fine being raised by confiscating 20 percent of every Jewish property. The Jews also had to repair all damages at their own cost.
As many as half of the 500,000 Jews in Germany in 1933 fled before the Holocaust.
The Holocaust (1940–1945)
The Nazi persecution of the Jews culminated in the Holocaust, in which approximately six million European Jews were deported and exterminated during the Second World War. On May 19, 1943, Germany was declared judenrein (clean of Jews; also judenfrei: free of Jews). It is believed that between 170,000 and 200,000 German Jews were killed. Many Jews were shielded from the labor camps by other German traders, unsympathetic to the Nazis and their policies.
Approximately 150,000 German Jews served in the German Wehrmacht, including decorated veterans and high-ranking officers, even generals and admirals. A great many of these men did not even consider themselves Jewish and had embraced the military as a way of life and as devoted patriots eager to serve a revived German nation. In turn, they had been embraced by the Wehrmacht, which prior to Hitler had given little thought to the race of these men but which was now forced to look deeply into the ancestry of its soldiers.[16]
Jews in Germany from 1945 to the unification
Most German Jews who survived the war in exile decided to remain abroad; however, a small number returned to Germany. Additionally, approximately 15,000 German Jews survived the concentration camps or survived by going into hiding. These German Jews were joined by approximately 200,000 displaced persons (DPs), eastern European Jewish Holocaust survivors. They came to Allied-occupied western Germany after finding no homes left for them in eastern Europe (especially in Poland) or after having been liberated on German soil. The overwhelming majority of the DPs wished to emigrate to Palestine and lived in Allied- and U.N.-administered refugee camps, remaining isolated from German society. After Israeli independence in 1948, most left Germany; however, 10,000 to 15,000 remained. Despite hesitations and a long history of antagonism between German Jews (Yekkes) and eastern European Jews (Ostjuden), the two disparate groups united to form the basis of a new Jewish community. In 1950 they founded their unitary representative organization, the Central Council of Jews in Germany.
Jews of West Germany
The Jewish community in West Germany from the 1950s to the 1970s was characterized by its social conservatism and generally private nature. Although there were Jewish elementary schools in West Berlin, Frankfurt, and Munich, the community had a very high average age. Few young adults chose to remain in Germany, and many of those who did married non-Jews. Many critics of the community and its leadership accused it of ossification. In the 1980s, a college for Jewish studies was established in Heidelberg; however, a disproportionate number of its students were not Jewish. By 1990, the community numbered between 30,000 and 40,000. Although the Jewish community of Germany did not have the same impact as the pre-1933 community, some Jews were prominent in German public life, including Hamburg mayor Herbert Weichmann; Schleswig-Holstein Minister of Justice (and Deputy Chief Justice of the Federal Constitutional Court) Rudolf Katz; Hesse Attorney General Fritz Bauer; former Hesse Minister of Economics Heinz-Herbert Karry; West Berlin politician Jeanette Wolff; television personalities Hugo Egon Balder, Hans Rosenthal, Ilja Richter, Inge Meysel, and Michel Friedman; Jewish communal leaders Heinz Galinski, Ignatz Bubis, Paul Spiegel, and Charlotte Knobloch (see: Zentralrat der Juden in Deutschland); and Germany’s most influential literary critic, Marcel Reich-Ranicki.
Jews of East Germany
The Jewish community of East Germany numbered only a few hundred active members. Most Jews who settled in the Soviet occupation zone or the German Democratic Republic did so either because their pre-1933 homes had been in eastern Germany or because they had been politically leftist before the Nazi seizure of power and, after 1945, wished to build an antifascist, socialist Germany. Most such politically engaged Jews were not religious or active in the official Jewish community. They included writers Anna Seghers, Stefan Heym, Jurek Becker, and composer Hanns Eisler.
Jews in the United Germany (post-1990)
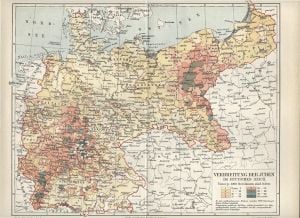
Today, Germany is home to a nominal Jewish population of more than 200,000; 108,000 are officially registered with Jewish religious communities. Most Jews in Germany are recent immigrants from the former Soviet Union. There is also a handful of Jewish families from Muslim countries, including Iran, Turkey, Morocco, and Afghanistan. Germany has the third-largest Jewish population in Western Europe after France (600,000) and Great Britain (300,000).[17] and the fastest-growing Jewish population in Europe in recent years. The influx of refugees, many of them seeking renewed contact with their Jewish heritage, has led to a renaissance of Jewish life on German soil. In 2002 a Reform rabbinical seminary, Abraham Geiger College, was established in Potsdam. In 2006, the college announced that it would be ordaining three new rabbis, the first rabbis to be ordained in Germany since 1942.
Partly owing to the deep similarities between Yiddish and German, Jewish studies has become a very popular subject for academic study, and many German universities have departments or institutes of Jewish studies, culture, or history. Active Jewish religious communities have sprung up across Germany, including in many cities where the previous communities were no longer extant or were moribund. Several cities in Germany have Jewish day schools, kosher facilities, and other Jewish institutions beyond synagogues. Additionally, as many of the Russian Jews were alienated from their Jewish heritage and unfamiliar or uncomfortable with Orthodox Judaism. American-style Reform Judaism, led by the Union of Progressive Jews in Germany, has emerged as a powerful and popular force in Germany, even though the Central Council of Jews in Germany and most local Jewish communities officially adhere to Orthodoxy. The unresolved tension between the re-emerging Reform movement in Germany and the official Orthodoxy is one of the most pressing issues facing the community at present.

An important step for the renaissance of Jewish life in Germany occurred when on January 27, 2003 German Chancellor Gerhard Schröder signed the first-ever agreement on a federal level with the Central Council, so that Judaism was granted the same elevated, semi-established legal status in Germany as the Roman Catholic and Evangelical Church in Germany, at least since the Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany of 1949.
In Germany it is a criminal act to deny the Holocaust or that six million Jews were murdered in the Holocaust (§130 StGB); violations can be punished with up to five years of prison. Although the number of right-wing groups has increased. Despite these facts, Israeli Ambassador Shimon Stein warned in October 2006 that Jews in Germany feel increasingly unsafe, stating that they “are not able to live a normal Jewish life” and that heavy security surrounds most synagogues or Jewish community centers.[18]Yosef Havlin, Rabbi at the Chabad Lubavitch in Frankfurt, does not agree with the Israeli Ambassador and states in an interview with Der Spiegel in September 2007 that the German public does not support far-right groups; instead, he has personally experienced the support of Germans, and as a Jew and rabbi he “feels welcome in his (hometown) Frankfurt, he is not afraid, the city is not a no-go-area”.[19]
A flagship moment for the burgeoning Jewish community in modern Germany occurred on November 9, 2006 (the 68th anniversary of Kristallnacht), when the newly constructed Ohel Jakob synagogue was dedicated in Munich, Germany. This is particularly crucial given the fact that Munich was once at the ideological heart of Nazi Germany. Jewish life in the capital Berlin is prospering, the Jewish community is growing, the Centrum Judaicum and several synagogues—including the largest in Germany—have been renovated and opened, and Berlin’s annual week of Jewish culture and the Jewish Cultural Festival in Berlin, held for the 21st time, featuring concerts, exhibitions, public readings and discussions[20][21] can only partially explain why Rabbi Yitzhak Ehrenberg of the orthodox Jewish community in Berlin states: “Orthodox Jewish life is alive in Berlin again. … Germany is the only European country with a growing Jewish community.”[22]
See also
- Martin Luther
- Holocaust
- Antisemitism
- AntiJudaism
Notes
- ↑ Migration to Germany (from former Soviet Union) Central Council of Jews in Germany Zentralrat der Juden in Deutschland. Retrieved December 16, 2007.
- ↑ S. M. Donovan, Bernardinus of Sileisa Catholic Encyclopedia Volume II, (NY: Robert Appleton Co, 1907) newadvent.org. Retrieved December 16, 2007.
- ↑ Martin Luther, “That Jesus was Born a Jews,” 199-229, Luther’s Works. Volume 45, edited by Walter Brandt, (Philadelphia: Mohlenberg Press, 1962), 229
- ↑ Martin Luther, “On the Jews and Their Lies,” 137-396, in Luther’s Works Volume 47, edited by Franklin Sherman, (Philadelphia: Mohlenberg Press, 1971), 268
- ↑ CHMIELNICKI, BOGDAN ZINOVI. Jewish Encyclopedia. Retrieved February 22, 2009.
- ↑ Rabbi Gershom
- ↑ Isadore Siungerm and Isaac Broydé, H. Arnheim "Arnheim, Heymann" Jewish Encyclopedia. Retrieved December 16, 2007
- ↑ I. Singer and H. Malter, "David Cassel" Jewish Encyclopedia Retrieved December 16, 2007
- ↑ J. Jacobs and I. Broydé, "Zomber, Berhard (Bär)" Berhard Bär Jewish Encyclopedia. Retrieved December 16, 2007
- ↑ Fritz B. Voll, Short Review of a Troubled History, 12 Jewish Christian Relations.net.
- ↑ "Introduction to Die Judischen Gefallenen," German Jewish Soldiers “Die Judischen Gefallenen” (The Jewish war dead) A roll of honor commemorating the 12,000 German Jews who died for their fatherland in World War I. Retrieved December 16, 2007.
- ↑ “About 10,000 volunteered for duty, and over 100,000 out of a total German-Jewish population of 550,000 served during World War One. Some 78 percent saw front-line duty, 12,000 died in battle, over 30,000 received decorations, and 19,000 were promoted. Approximately 2000 Jews became military officers and 1200 became medical officers.” (Bryan Rigg. Hitler’s Jewish Soldiers. (Lawrence, KS: University Press of Kansas, 2002. ISBN 9780700611782), 72)
- ↑ " “Deutsche Jüdische Soldaten” (German Jewish Soldiers), Bavarian National Exhibition “Deutsche Jüdische Soldaten” (German Jewish soldiers) Retrieved December 16, 2007.
- ↑ Frank Bajohr, "The “Folk Community” and the Persecution of the Jews: German Society under National Socialist Dictatorship, 1933–1945." Holocaust Genocide Studies 20 (Fall 2006): 183–206.
- ↑ S. Friedländer, Chapter 3: Redemptive Anti-Semitism Retrieved December 16, 2007. S. Friedländer. Nazi Germany and the Jews, Vol. I: The Years of Persecution 1933-1939. (New York: 1997), 73–112. (Yad Vashem History of the Holocaust, a collaboration between the Yad Vashem Holocaust Remembrance Authority in Jerusalem and Drew University, Madison, New Jersey.
- ↑ [1]
- ↑ Die Welt November 17, 2004, “Oberrabbiner tagen erstmals in Berlin.” Retrieved December 16, 2007. (in German)
- ↑ Berlin police say 16 arrested during neo-Nazi demonstration, Oct. 22, 2006, [2] International Herald Tribune - Europe. Retrieved February 22, 2009.
- ↑ Der Spiegel September 12, 2007, “Wir dürfen uns auf keinen Fall verstecken” Retrieved December 16, 2007.
- ↑ "Germany's Largest Synagogue Officially Re-opened," Die Bundesregierung (Federal government of Germany) August 31, 2007, Germany’s largest synagogue officially reopened.
- ↑ Toby Axelrod, January 21, 2000, Cantor who led Berlin’s Jews for past 50 years dies Jewish News Weekly. Retrieved December 16, 2007.
- ↑ Katrin Schoelkopf, November 18, 2004, “Rabbiner Ehrenberg: Orthodoxes jüdisches Leben ist wieder lebendig in Berlin” (Rabbi Ehrenberg: Orthodox Jewish life is alive again in Berlin). WELT online, Retrieved December 16, 2007.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Bajohr, Frank, "The “Folk Community” and the Persecution of the Jews: German Society under National Socialist Dictatorship, 1933–1945." Holocaust Genocide Studies 20 (Fall 2006): 183–206.
- Dimont, Max I. Jews, God, and History, second ed. (1962). Signet Classics, 2004. ISBN 978-0451529404.
- Elon, Amos. The Pity of It All: A History of Jews in Germany, 1743-1933. New York: Metropolitan Books, 2002. ISBN 9780805059649.
- Friedlander, Sau. Chapter 3 in: Nazi Germany and the Jews, Vol. I - The Years of Persecution 1933-1939. New York: Harper Perennial, 1997. ISBN 0060928786.
- Geller, Jay Howard. Jews in Post-Holocaust Germany. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2005. ISBN 978-0521833530.
- Kaplan, Marion A. Jewish Daily Life in Germany, 1618–1945. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2005. ISBN 978-1423720706.
- Luther, Martin. Luther’s Works. Volume 45, edited by Walter Brandt, Philadelphia: Mohlenberg Press, 1962.
- Luther, Martin. Luther’s Works. Volume 47, edited by Franklin Sherman, Philadelphia: Mohlenberg Press, 1971.
- Mendes-Flohr, Paul, and Judah Reinharz. The Jew in the Modern World: A Documentary History. Oxford University Press. New York, 1995.
- Meyer, Michael A., ed. German–Jewish History in Modern Times. vols. 1–4. New York: Columbia University Press, 1996–1998. ISBN 780231074728
- vol. 1 Tradition and Enlightenment, 1600–1780
- vol. 2 Emancipation and Acculturation, 1780–1871
- vol. 3 Integration in Dispute, 1871–1918
- vol. 4 Renewal and Destruction, 1918–1945
- Peck, Jeffrey. Being Jewish in the New Germany. New Brunswick, NJ: Rutgers University Press, 2006. ISBN 9780813537238
- Rigg, Bryan. Hitler’s Jewish Soldiers. Lawrence, KS: University Press of Kansas, 2002. ISBN 9780700611782.
- Voll, Fritz B. A Short Review of a Troubled History Jewish Christian Relations.net. Retrieved December 16, 2007.
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.